Cloud migration isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a critical transformation strategy for enterprises looking to scale, cut costs, and innovate. Whether you’re moving from legacy on-premise systems to the cloud or shifting between cloud platforms, a well-executed migration can improve agility, performance, and business continuity.
However, without a structured plan, cloud migration can become complex, expensive, and disruptive. This guide will walk you through every step of the cloud migration journey—so you can make the move with confidence.
What is Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration is the process of moving your digital assets — like applications, data, and workloads — from your local servers or data centers to cloud-based infrastructure (e.g., AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, etc.).
For many businesses, the goal is to:
- Cut infrastructure costs
- Improve performance
- Enhance security
- Enable remote work and collaboration
- Scale quickly without heavy hardware investment
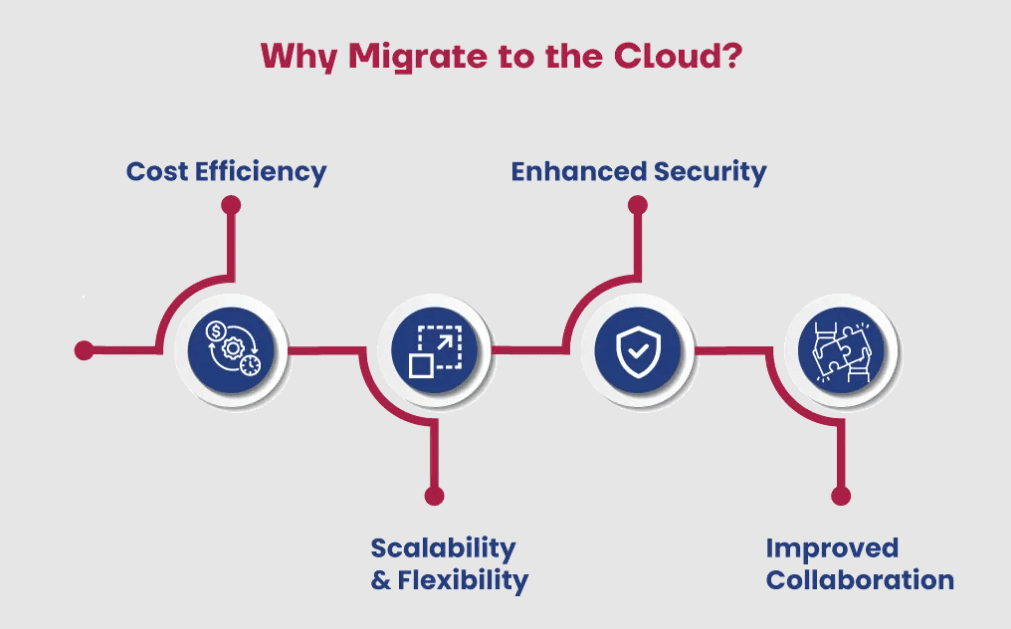
Why Migrate to The Cloud?
Here are some of the top benefits enterprises gain by moving to the cloud:
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for what you use — no need for expensive hardware or physical space.
- Scalability & Flexibility: Easily increase or decrease resources as needed.
- Remote Access: Work from anywhere, anytime.
- Security: Cloud providers offer enterprise-grade security and compliance features.
- Innovation: Access to the latest tools, analytics, and AI features without massive investment.
But to get these benefits, you need a solid plan.
Step-by-Step Guide For Cloud Migration
Step 1: Define Your Goals and Business Needs
Before moving anything to the cloud, ask:
- Why are we migrating?
- What problems are we trying to solve?
- Which systems or apps are mission-critical?
Examples of goals:
- Reduce data center costs by 30%
- Improve system availability to 99.9%
- Enable global teams to access systems securely
Having clear business objectives helps guide your entire migration strategy.
Step 2: Audit Your Current Infrastructure
Create a full inventory of:
- Applications
- Databases
- Servers
- Storage
- Network dependencies
This audit will help you understand:
- What can be moved
- What needs to be replaced or retired
- Which systems have dependencies that must be migrated together
Also evaluate:
- App usage patterns
- Performance bottlenecks
- Security risks in the current setup
Step 3: Choose the Right Cloud Environment
There are three main cloud models:
- Public Cloud – Services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, shared with other customers.
- Private Cloud – Dedicated infrastructure, either on-premise or hosted by a provider.
- Hybrid Cloud – A mix of both, often used when some apps must stay on-premise for legal or technical reasons.
Choose based on:
- Your budget
- Compliance needs
- App sensitivity and security
- Performance requirements
Step 4: Select a Migration Strategy
There are several common approaches, often called the “6 Rs” of Cloud Migration:
- Re-host (Lift and Shift): Move apps as-is to the cloud. Fast, but may not be fully optimized.
- Replatform: Make minor updates to improve performance in the cloud.
- Refactor: Rewrite parts of the app to take full advantage of cloud capabilities.
- Repurchase: Replace legacy apps with SaaS options (e.g., moving from an old CRM to Salesforce).
- Retain: Keep some systems on-premise (due to regulation or performance).
- Retire: Shut down outdated or unused systems.
Choose what works best for each application or workload.
Step 5: Plan for Security and Compliance
Security must be part of the migration process, not an afterthought.
Things to consider:
- Data encryption (at rest and in transit)
- Access control and identity management
- Backup and disaster recovery plans
- Compliance with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, etc.
Work closely with your IT security and compliance teams to ensure everything is in order.
Step 6: Build a Detailed Migration Plan
Your plan should include:
- Migration timelines
- App dependencies
- Downtime windows (if needed)
- Roles and responsibilities
- Risk mitigation strategies
Test everything before going live. Create a migration “runbook” that your team can follow step-by-step.
Step 7: Execute the Migration
Start with less critical systems to test your process.
Follow your runbook closely:
- Move data and apps
- Monitor performance
- Verify that everything works
- Rollback quickly if needed
Use migration tools offered by cloud providers (like AWS Migration Hub or Azure Migrate) to automate parts of the process.
Step 8: Monitor and Optimize
Once systems are live in the cloud:
- Set up dashboards to track performance
- Monitor costs and usage
- Right-size resources (scale up/down as needed)
- Use analytics to spot inefficiencies
Cloud isn’t “set it and forget it.†Continuous monitoring helps you get the most out of your investment.
Common Challenges and How to Avoid Them
Challenge 1: Unclear Goals
Solution: Define clear business objectives from the start.
Challenge 2: Unexpected Costs
Solution: Use cloud cost calculators and budgeting tools to track expenses.
Challenge 3: Downtime
Solution: Schedule migrations during off-hours and have a rollback plan.
Challenge 4: Security Risks
Solution: Encrypt data, use multi-factor authentication, and review access controls.
Conclusion: Cloud Migration is a Journey – Plan It Right
Cloud migration is more than just a technology upgrade — it’s a business transformation. When done right, it improves performance, saves money, and sets your business up for future growth.
But rushing in without a plan can lead to downtime, cost overruns, and frustrated teams. By following a step-by-step strategy, your enterprise can move to the cloud with confidence — and start reaping the benefits from day one.
Whether you’re just starting or looking to expand your cloud presence, having the right roadmap makes all the difference.
