
In today’s fast-paced digital world, your business network and online services need to be available 24/7 — with minimal downtime and maximum efficiency. Whether you’re running a company website, business applications, or internal systems, two key strategies can help maintain performance and uptime: Load Balancing and Failover.
But what do these terms mean — and which one is right for your business? Let’s break it down in simple terms.
Understanding Load Balancing?
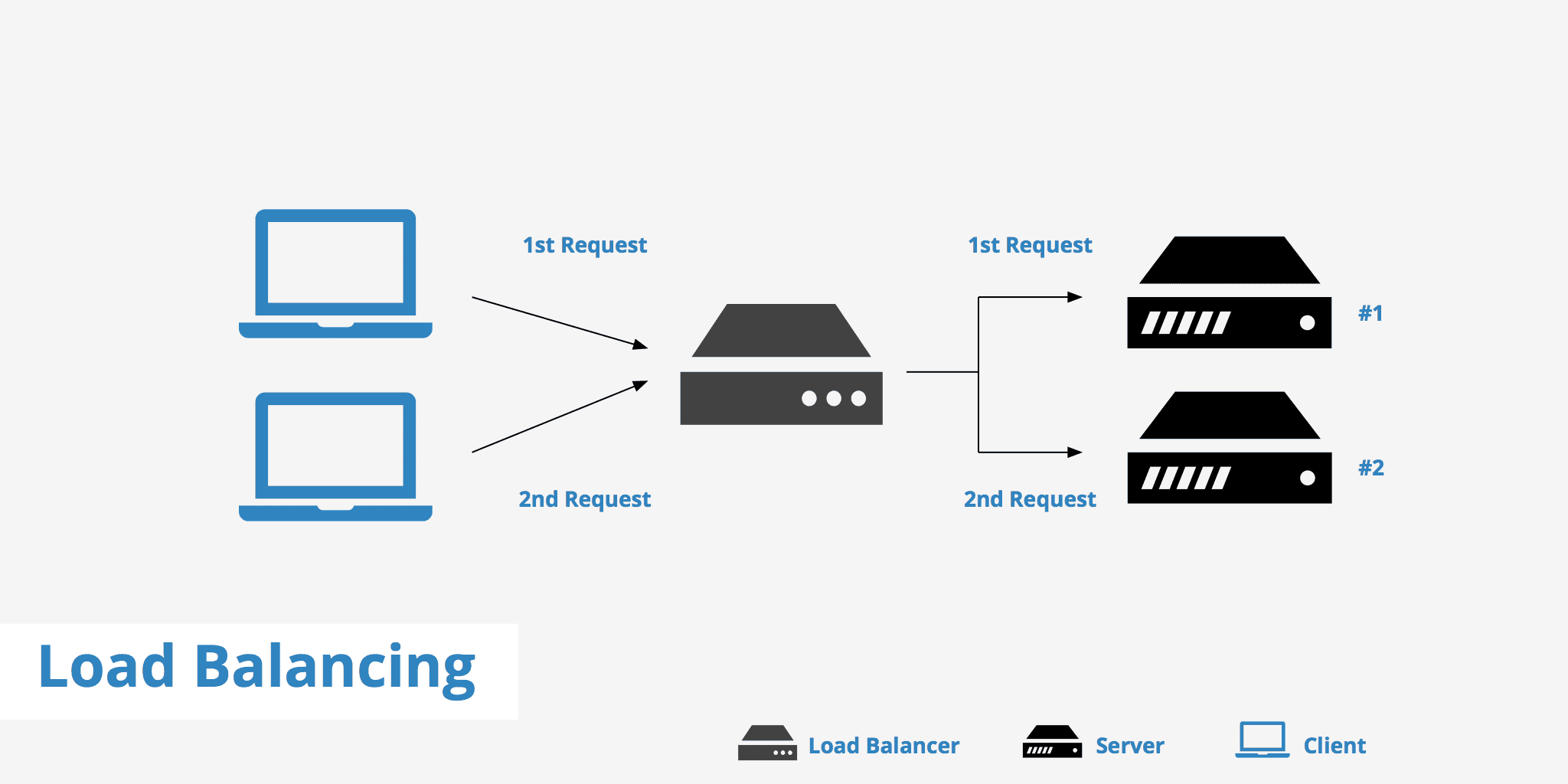
Load balancing is a technique that distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers or resources. The primary goal is to ensure no single server becomes a bottleneck, thereby improving performance, reliability, and scalability.
How Load Balancing Works:
- A load balancer sits in front of your server pool and directs client requests based on pre-defined rules (e.g., round robin, least connections, geographic proximity).
- It constantly monitors the health of servers and only routes traffic to those that are functioning properly.
- This setup improves response times and allows for horizontal scaling by adding more servers as needed.
Benefits of Load Balancing:
- Enhanced performance and reduced latency
- High availability by routing around failed servers
- Seamless scaling of applications during peak usage
- Balanced resource usage, preventing overload
Why It Matters:
- Prevents any single server from getting overloaded
- Improves performance, scalability, and reliability
- Ensures users get faster response times
Real-World Example:
An e-commerce website uses three web servers. When a customer visits the site, the load balancer directs their request to the least-busy server. If one server is slow or under maintenance, traffic is automatically redirected to others.
Understanding Failover
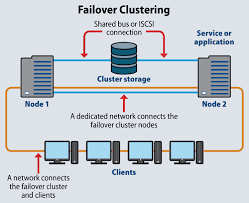
Failover is a backup operational mode in which the functions of a system switch to a standby system or component when the primary one fails. It’s a reactive mechanism, focused on minimizing downtime in the event of a failure.
How Failover Works:
- A secondary (standby) server is configured to take over automatically when the primary server fails.
- The switch can be automatic or manual, depending on the setup.
- Common in systems where continuous uptime is critical, such as databases, DNS services, and disaster recovery solutions.
Benefits of Failover:
- Guarantees business continuity during unexpected failures
- Protects against data loss and system outages
- Often used in combination with backup solutions and disaster recovery plans
Why It Matters:
- Minimizes downtime in the event of hardware failure or crashes
- Ensures business continuity
- Often used in critical systems like databases, email servers, or internet connectivity
Real-World Example:
Your company has a primary internet connection. If it goes down, the system automatically switches to a backup ISP — so your operations continue uninterrupted.
Load Balancing vs. Failover: Key Differences
| Feature | Load Balancing | Failover |
| Purpose | Distribute workload across multiple systems | Provide a backup when the primary system fails |
| Usage | Performance optimization | High availability and disaster recovery |
| Operational Mode | All systems run concurrently | Backup system is on standby (or passive mode) |
| Downtime Handling | Prevents overload, reducing risk of failure | Kicks in after a failure to maintain service |
| Best For | Websites, cloud apps, large-scale services | Critical services like databases, firewalls, ISPs |
| Cost | May involve more hardware/resources upfront | Can be more affordable if only one backup is needed |
Which One is Right for Your Business?
Choosing between load balancing and failover depends on your business goals, infrastructure, and risk tolerance:
Choose Load Balancing If:
- You handle high volumes of concurrent users or data
- Application performance and fast response times are critical
- You want to scale services efficiently and support redundancy
- You aim for continuous availability through distribution, not just backup
Choose Failover If:
- You need guaranteed uptime and rapid recovery from failures
- You run mission-critical systems like databases, payment gateways, or healthcare applications
- Your architecture is more centralized and can’t support distributed traffic handling
- You want a simple, cost-effective solution to protect against hardware or software failure
Why Not Both?
In many enterprise environments, load balancing and failover are used together. Load balancers can handle traffic under normal conditions, while failover mechanisms ensure service continuity during complete outages.
For instance, you can have:
- A primary data center with load balancing across multiple servers
- A secondary data center that acts as a failover site in case of a disaster
This layered approach delivers both performance and resilience.
Final Thoughts
Both load balancing and failover play vital roles in building a resilient IT infrastructure. The right choice (or combination) ensures your business stays online, fast, and secure — even when things go wrong.
To determine the right approach, assess your business needs, customer expectations, and technical capabilities. Often, a hybrid solution combining both methods offers the best of both worlds—ensuring your services stay fast, reliable, and always available.
